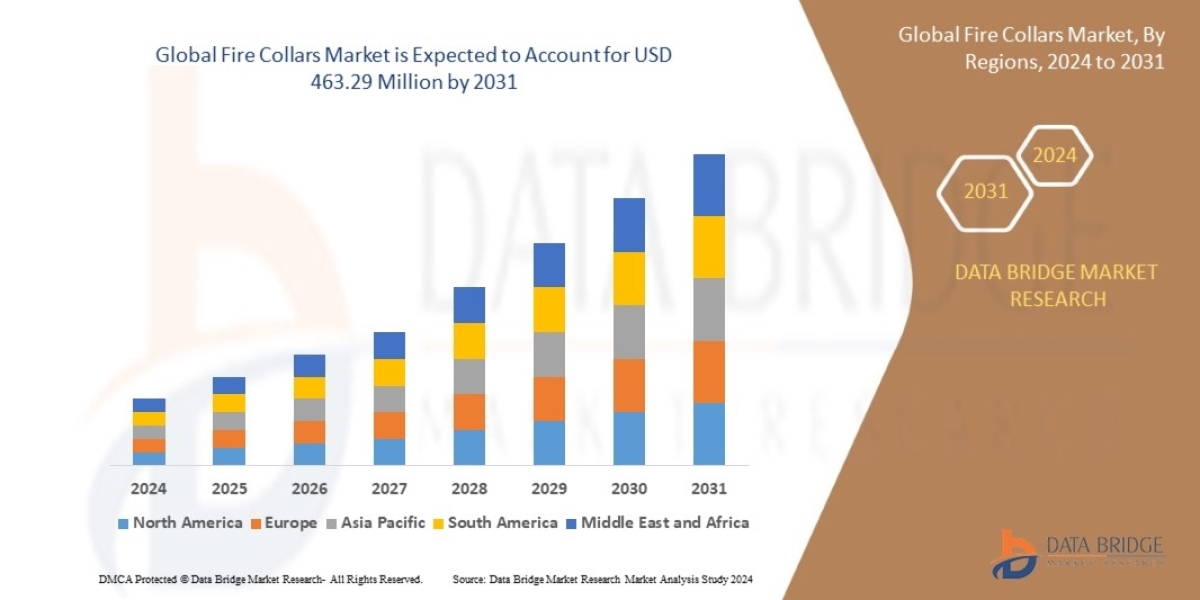
Microinsurance: Empowering Financial Protection for Low-Income Communities
Microinsurance is a powerful financial tool designed to provide insurance coverage to low-income individuals and families who are typically underserved by traditional insurance markets. With affordable premiums and simplified products, microinsurance helps protect vulnerable populations against specific risks such as illness, crop failure, natural disasters, and death, offering them a safety net to recover from financial shocks.
What is Microinsurance?
Microinsurance Market Size refers to insurance products tailored to the needs of low-income populations. It offers coverage in exchange for low premiums, often collected on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis. These policies are generally more accessible, easier to understand, and focused on high-impact events, such as hospitalization, property loss, or weather-related incidents that can drastically affect the financial stability of poor households.
Key Features of Microinsurance
- Low Premiums: Designed to be affordable for those with limited incomes.
- Simple Terms: Policies are straightforward, with fewer exclusions and minimal paperwork.
- Targeted Coverage: Focuses on essential needs like health, life, agriculture, or property insurance.
- Flexible Payments: Premiums can be paid via mobile money or in cash, often in small increments.
- Community-Based Delivery: Often distributed through cooperatives, NGOs, or microfinance institutions.
Types of Microinsurance Products
- Health Microinsurance: Covers medical costs for minor or major illnesses and hospital stays.
- Life Microinsurance: Provides financial support to beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder's death.
- Agricultural Microinsurance: Protects farmers against crop losses due to drought, floods, or pests.
- Property Microinsurance: Offers coverage for damage or loss of small-scale homes and businesses.
- Disability and Accident Insurance: Assists in case of temporary or permanent disability due to accidents.
Importance of Microinsurance
- Reduces Poverty: Helps families avoid falling deeper into poverty when emergencies strike.
- Enhances Resilience: Builds financial resilience and promotes long-term economic stability.
- Improves Access to Services: Encourages access to healthcare and education through financial security.
- Fosters Financial Inclusion: Connects underserved populations with broader financial services.
Challenges in Microinsurance
- Low Awareness and Trust: Limited understanding and skepticism about insurance can hinder adoption.
- Distribution Barriers: Reaching remote or rural areas remains a logistical challenge.
- Sustainability: Balancing affordability with profitability is complex for insurers.
- Data and Claims Management: Difficulties in tracking and verifying claims efficiently in low-resource settings.
The Role of Technology
Technology is revolutionizing microinsurance by making enrollment, premium collection, and claims processing faster and more efficient. Mobile-based platforms, satellite data for weather tracking, and blockchain for secure transactions are some innovations enhancing transparency and accessibility in microinsurance programs.
Conclusion
Microinsurance is a vital instrument in bridging the protection gap for low-income populations. By offering tailored, affordable coverage, it plays a crucial role in enhancing financial resilience, promoting inclusive growth, and reducing vulnerability among the world’s most economically disadvantaged groups.
Related Report -